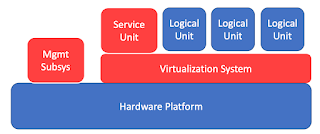
Virtualization Security: An Overview
Virtualization Security is a technology that enables multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server or host computer. Each operating system running in a virtual machine (VM) uses its own set of virtualized hardware (e.g., virtual CPUs, virtual storage devices) and is isolated from other VMs running on the same host. This provides benefits such as higher hardware utilization, better manageability, and easier disaster recovery. However, virtualization also presents new security challenges that organizations need to address to protect their data and systems.
Request To Free Sample of This Strategic Report:
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/virtualization-security-market-942
The following are some of the common security risks associated with virtualization:
-
Inter-VM attacks Since virtual machines on a single host share hardware resources, one VM can potentially access or compromise another VM running on the same host if a vulnerability exists in the virtualization software. For example, an attacker may exploit a flaw in the virtual networking stack to gain access to other VMs’ traffic.
-
Data leakage Information leakage can occur when virtual machines share a common host and are connected to the same network. If a VM examines network traffic and detects sensitive information (such as passwords or confidential data), it could be intercepted by an attacker.
-
VM sprawl If virtual machines are created and destroyed frequently, it can be difficult for IT staff to manage them effectively. Abandoned VMs can become a security risk if they are not properly de-provisioned or decommissioned.
-
Hypervisor attacks A hypervisor is a software layer that runs between the physical server and the virtual machines it hosts. If an attacker gains access to the hypervisor, they can potentially gain control of all the virtual machines running on the host.
To minimize these risks, organizations need to implement a range of security controls tailored to their needs. Here are some best practices that can help to ensure virtualization security:
-
Use secure hypervisors Ensure that the hypervisor is regularly patched and updated with the latest security fixes. Ideally, only use hypervisors that are certified against common security standards such as Common Criteria or ISO 27001.
-
Segment virtual networks Segmenting virtual networks can reduce the risks of an attacker being able to access other virtual machines. Use firewalls and virtual LANs to break up the virtual network, and use access controls to control who or what can access each segment.
-
Use IAM controls Identity and Access Management (IAM) controls can help to ensure that only authorized users have access to virtual machines and data. This includes using strong authentication, access